It might seem daunting, time consuming & prohibitive for smaller practices, to implement BIM. Not with Driving Vision!
This article is part of a blog series on new building materials used in the construction industry, exploring what they are, why they are cheaper and more durable than traditional materials.
A lot of materials are used in the construction industry such as wood, concrete, and plastic. Sadly, many of these have an ecological, economic, and/or geopolitical impact. We need to find alternative solutions for these materials, so the construction industry can contribute to the resolution of these problems.

Historically clay, natural stones, or wood have been the base of materials used in the construction industry. For example, the Great Wall of China was constructed 600 years ago mainly with earth and stones. By mixing sticky rice flour and slaked lime as a base for their mortar to bind the bricks together and avoid growing weeds.
Lately, sand and lime have been introduced into the fabric of buildings and structures. All these materials are refined to produce cement, concrete, or glass.
Building materials can be either recycled or not
Materials are classified as organic or inorganic.
Organic building materials derive from natural sources and are renewable, including:
Inorganic materials are used in building and infrastructure construction. They include:

In the construction industry, materials are governed by national and international standards and codes, depending on the types of structures that are built.
Project owners could ask their architects to determine which materials should be used, based on their artistic preferences, project deadlines, and cost considerations.
Some, of the most frequently used construction materials are discussed below.
Masonry accumulates pieces of material that are held one above the other with mortar, to create a structure. It uses bricks which are rectangular blocks traditionally made from heated and dry clay. They:
Pros: Bricks can be assembled by low-skilled laborers, and/or robots, as their shapes and sizes are homogeneous.
Cons: Bricks are vulnerable to seismic destruction and break easily.
Concrete is one of the most frequently used building materials. It is made of fine and coarse aggregate, mixed and glued with cement or water.
Concrete can be:
Pros: It can be compacted in all sorts of shapes, is versatile, and is a hard material with good thermal storage capacity and sound insulation.
Cons: Poor CO2 emission which is bad news for the climate crisis.
Much like concrete, this is made of coarse aggregate, mixed and glued with cement or water. However, cured under heat and pressure in an autoclave, which makes it lighter than regular concrete. It can be used as a brick alternate product
Pros: high thermal insulation; lightweight material.
Cons: low sound insulation; absorbs water.
Plastics have a bad reputation as being unsustainable, but is it well deserved? We don't think so and here's why. They:
They can be used in many areas:
Pros: weightless and versatile.
Cons: based on natural raw materials, poor image of sustainability.
Clays are made up of various minerals which are classified as hydrous aluminum phyllosilicates.
These minerals may be iron, alkali metals, alkaline earth, or other cations found in the surrounding soil. It is a natural building material considered well-suited from a sustainability point of view.
Using local soil in a 3D printer could soon be an alternative to concrete. If the researchers find a solution to produce concrete made of all soil types, en mass, the construction industry could reduce its gas emissions by:
Clay building materials are:
Clay Building materials are used in the form of:
Pros: accessible; low CO2 emissions.
Cons: few specialists around; takes ages to dry.
Steel is a composite material made from alloys of iron and carbon.
Steel is:
Steel is used in:
Pros: speed of construction, safety, aesthetics.
Cons: break down at high-temperature levels, poor fire resistance.
Stone is the most durable building material. It is formed by compacting grains or pieces of any kind of existing rock material.
Stone is used in:
Stones have the following features:
The most used stone in construction are:
Pros: cheap except if you need unique finishes.
Cons: difficult to work with as they are heavy, bad for insulation in cold environments
Wood is the oldest construction material. Depending on the tree species you choose, they may contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorous.
Wood is:
Wood is used in areas like:
• walls, floors, and ceilings • door and window frames • building and bridge structures • thermal insulation • acoustic insulation
Pros: good thermal conductivity, sound insulation, sustainable, recyclable.
Cons:has natural enemies like woodworms.
Transparent, recycled wood, could replace window glass, and is stronger than most metals, despite its lightness.
In our previous post we discussed the various types of sustainable building materials. Please read the article to find out how the worldwide housing crises and global climate change, encourage the building industry to find ways of:
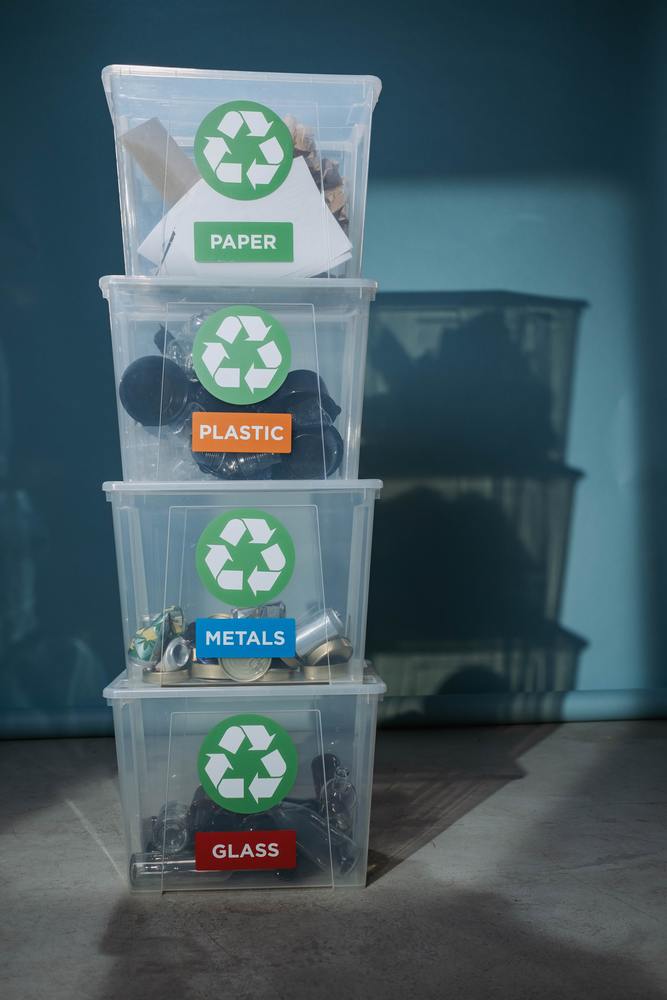

Any construction project you start, either new or renovation, requires that you select some building materials. If - like many in our industry - you have a habit of sending quotes before checking what types of materials should be included, you are at risk of having priced it incorrectly. Let's see how you can decide which materials are right for your project:
It would depend on:
In collaboration with the engineers, the client, and the architect, you should consider:
This will help you to select the best possible building materials for your project which will be:
Throughout their lifespan, all building materials:
During the selection of your building materials, considering all the above implications on the environment, without compromising the quality of the product, is important to help you meet your societal and sustainable responsibilities.
Your supply chain management system should help you to sequence your construction actions, and the impact the lead time of procuring a material will have on your project’s deadlines.
The quality of your chosen building materials has an impact on:
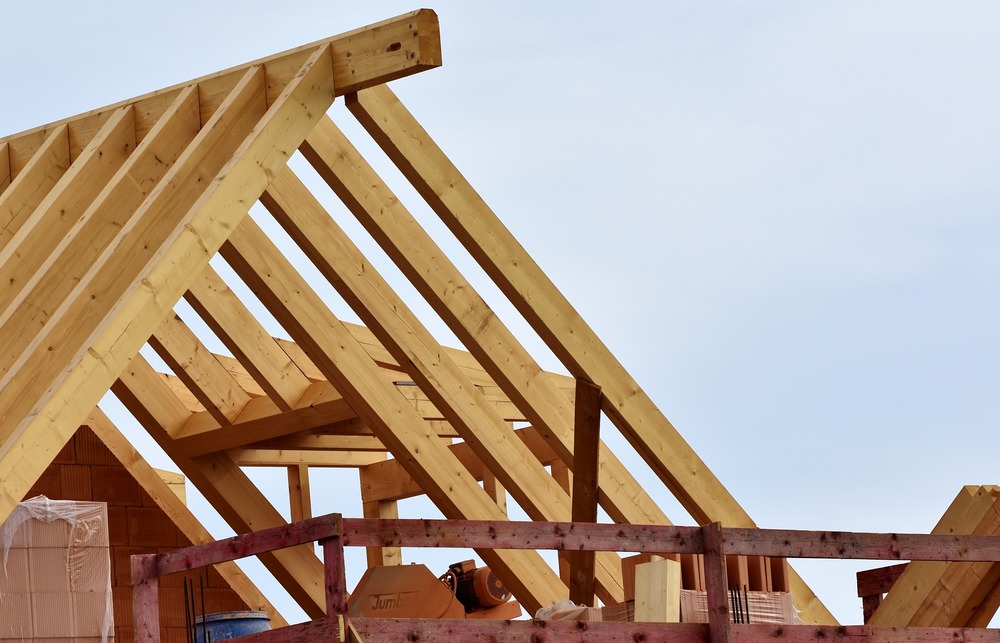

All building materials are used in specific fields or operations. For example:
Concrete or bricks are normally used to construct a building for:
To insulate a building for heat and/or sound you can use squeezed polystyrene. For example:
Fire retardant building materials are made of combustible components including:
You should avoid highly flammable building materials like:
To build environmentally friendly construction, the building materials should:

Long delivery times and inflation for building materials continue to be challenging around the world in 2023.
Positive building materials trends are:
Most firms intend to establish their best practices, but work gets in the way and they are never created.
Driving Vision's BIM expertise diagnostic looks at how you can eliminate waste (time and material), and improve your margins and the quality of the information provided at the design and construction phases.
A Driving Vision expert will conduct the interviews online and will issue a report and discuss our findings with you. Together we will decide the best way to implement the solutions at your pace and according to your budget.
Implementing BIM can be daunting, but Driving Vision is here to help you at the pace you are comfortable with. Get started by getting in touch now
Of practices using BIM made positive ROI
Of practices using BIM improved health and safety
Of practices using BIM decreased errors and omission
Of practices using BIM enhanced their practice image
Of practices using BIM claimed less litigations
Of practices using BIM reduced rework
It might seem daunting, time consuming & prohibitive for smaller practices, to implement BIM. Not with Driving Vision!